It’s a sexually transmitted infection caused by pubic lice that belong to the family arthropoda, subfamily mandibulata, class insecta. Its transmission has been related to poor hygienic conditions.
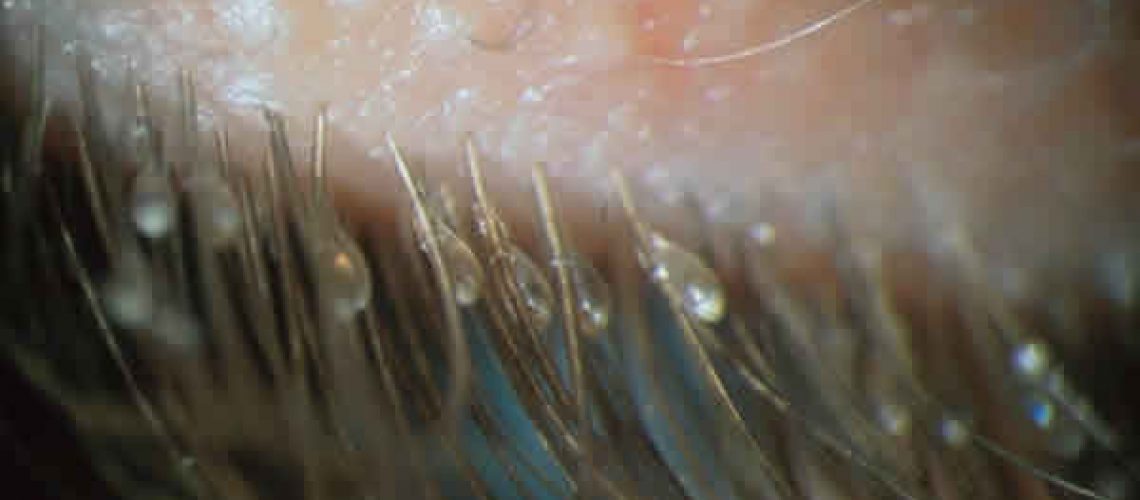
Lice have a small/square head, with antennae and two eyes. They have denticles that allow them to attach to the skin, which will later be pierced by means of stylets, through which the blood will be absorbed thanks to a pharyngeal pump. Their saliva is composed of anticoagulant substances that facilitate the task.
For its correct diagnosis, the use of a slit lamp is very important. In the biomicroscopy, palpebral scratching lesions and violaceous lesions near the base of the eyelashes that correspond to the bite areas will be observed.
We must have a high level of suspicion and look for the parasites, because on many occasions they will remain immobile and strongly adhered to the skin-eyelash interface, so they can easily go unnoticed or be confused with a scale of chronic anterior blepharitis. Sometimes the parasites will contain blood or feces in their digestive tract, which will be visible due to the transparency of the insect.
The treatment is not always easy. All lice should be mechanically removed, especially adults and females, because if only one fertilized adult female is left, a recurrence will occur in a few weeks. This can be a very laborious task, since they are strongly adhered to the eyelashes, sometimes being necessary to cut the eyelashes themselves.
Its treatment also involves taking a single dose of ivermectin, good eyelash hygiene, use of Vaseline to suffocate the rest of the lice, antibacterial ointments, cryotherapy or the Argon Laser.