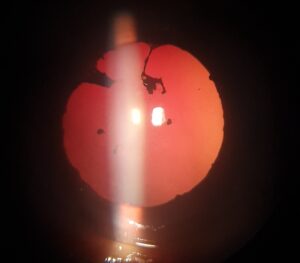
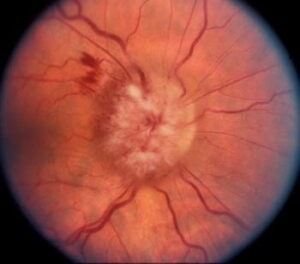
Chronic diabetes impairs the body’s capacity to make or use insulin, which controls blood sugar levels. Over time, severe health issues, such as damage to the eyes, can be brought on by high blood sugar levels. The following is a detailed account of how diabetes affects your eyes:
Diabetic Retinopathy:
This is the most common diabetic eye disease and a leading cause of blindness in adults. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive part of the eye. As a result, the blood vessels can leak fluid or bleed, leading to vision loss.
Cataracts:
People with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts at an earlier age than those without diabetes. Cataracts are cloudy areas in the lens of the eye that can blur vision.
Glaucoma:
People with diabetes are also at increased risk of developing glaucoma, which is a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss.
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME):
This is a condition where fluid accumulates in the macula, the central part of the retina, leading to swelling and vision loss. DME is a common complication of diabetic retinopathy.
Dry Eye Syndrome:
People with diabetes are also more likely to experience dry eye syndrome, a condition where the eyes do not produce enough tears to keep them moist, leading to discomfort, itching, and burning.
To protect the eyes from the effects of diabetes, people with the condition should:
- Maintain good blood sugar control: Keeping blood sugar levels within a target range can reduce the risk of diabetic eye disease.
- Have regular eye exams: People with diabetes should have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year to detect and treat diabetic eye diseases early.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of diabetic eye disease and other complications.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating a diet according to your lifestyle with a proper balance of macronutrients, high density low calorie foods can help manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Avoid high calorie low density food.